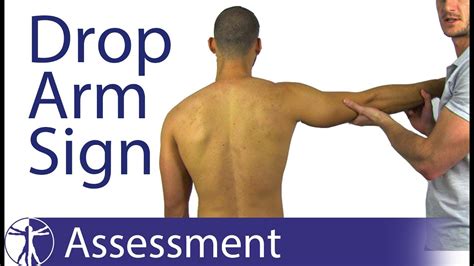
shoulder supraspinatus tear test|full thickness tear supraspinatus : exporters The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus [1]. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder .
Canterbury Park does not control and is therefore not respon.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Watch Tobias Menzies's Penis, Sexy scene on AZNude for free (1 minute and 36 seconds).
Supraspinatus Test. The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° forward flexion. From this position, we will ask the .
This test is done having your patient lie prone on their stomach. Next, flex the .A supraspinatus tear is a tear or rupture of the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle. The supraspinatus is part of the rotator cuff of the shoulder. Most of the time, it is accompanied by another rotator cuff muscle tear .Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive .
They'll also test the strength of the muscles around your shoulder and in your arms. Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X .
The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus [1]. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder . Rotator cuff tears are common injuries caused by damage to the muscles or tendons that stabilize your shoulder joint. They can be diagnosed by using a number of physical tests and imaging .This page describes the Drop Arm Test, a common test for a supraspinatus tear and/or rotator cuff tear. A video demonstration is included.
Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder. Treatment can be nonoperative .Most tears occur in the supraspinatus tendon, but other parts of the rotator cuff may also be involved. In many cases, torn tendons begin by fraying. As the damage progresses, the tendon can completely tear, sometimes with lifting a .
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.
Symptoms of a supraspinatus tendon tear. Symptoms of a supraspinatus tear include: Sharp pain in the shoulder at the time of injury. Pain when the arm is rotated outwards and upwards. Increased pain and .Most tears occur in the supraspinatus tendon, but other parts of the rotator cuff may also be involved. In many cases, torn tendons begin by fraying. . If you have a degenerative tear in one shoulder, there is a greater likelihood of a . Hawkins' test: Forward flexion of the shoulder to 90 degrees and internal rotation: . Often, the arm will drop to the side if the patient has a rotator cuff tear or supraspinatus dysfunction . This common shoulder disorder is often caused by repetitive overhead motions in jobs or sports. Extensive rotator cuff tears may require surgery. . Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as arthritis. Ultrasound.
Definition/Description [edit | edit source] Supraspinatus tendinopathy is a common and disabling condition that becomes more prevalent after middle age and is a common cause of shoulder pain.A predisposing factor is resistive overuse.. The supraspinatus tendon of the rotator cuff is involved and affected tendons of the musculoskeletal system and becomes degenerated, most .
supraspinatus tear test pdf
Rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young patients as well as degenerative disease in the elderly patient. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but .
Your healthcare provider may perform the drop arm test if they think you may have a rotator cuff tear in your shoulder. For this test, the provider will lift your arm out to the side of your body while keeping it straight. . Pain or weakness indicates a positive test for a possible supraspinatus tear or problem. Tests for Frozen Shoulder .Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Empty Can Test, also known as the Jobe or Supraspinatus test, is used to assess for lesions of the rotator cuff, specifically the supraspinatus muscle and supraspinatus tendon.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patients arm is actively abducted to 90 o; The examiner applies downward resistance to the abducted arm; With the patient's hand in . Primary care, sports medicine, and orthopedic surgeons commonly manage shoulder injuries and shoulder pain. Some reports in the literature cite that up to half of the clinical shoulder complaints are handled in a single visit by a primary care provider.[1] Rotator cuff pathologies are one common source of shoulder complaints. The rotator cuff consists of .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. This is a shoulder special test which is meant to assess the integrity, and tears, of the supraspinatus (SSP) and infraspinatus muscles (muscles which collectively contribute to the rotator cuff complex). This test can also be used for the clinical examination of a shoulder impingement syndrome (SIS).. Another name for this test is the Infraspinatus Spring .
Test Item Cluster: This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests are negative, the negative likelihood ratio is 0.16. The Neer sign and the Hawkins-Kennedy sign, commonly used to diagnose subacromial impingement, have a high sensitivity of 75–88% for supraspinatus tears.[18,19,20,21] However, these signs are characterized by a lack of specificity (<40%).[20,21] The transdeltoid palpation test, first described by Codman in 1934, has been used to diagnose .The Empty Can Test, along with the Full Can Test is a commonly used orthopedic examination test for supraspinatus impingement or integrity of the supraspinatus muscle and tendon. The test is also sometimes called the Empty Beer Can Test. The supraspinatus is one of the four rotator cuff muscles. Involved Structures. supraspinatus tendon Test Yourself for Supraspinatus Tear. There are some tests, however, that you can perform yourself to see if your supraspinatus is involved – the Zero Degree Abduction Test and the Drop Arm Sign. . Move through the exercises, advancing when you feel no pain and feel .
A partial tear may require only a trimming or smoothing procedure called a débridement. A full-thickness tear, which usually means the tendon is torn from its insertion on the humerus (the most common injury), is repaired directly to . Acute supraspinatus tears and degenerative supraspinatus tears. An acute tear of the supraspinatus muscle can occur alongside injuries like shoulder dislocation, clavicle fractures, or other rotator cuff injuries that .For detecting a supraspinatus tear the test has a sensitivity of 18.7% and a specificity of 100%, 4 this means if the test is positive it is highly likely that the patient has a tear. . Shoulder injury presentations are common in the general practice setting and most can be effectively managed at .
Supraspinatus tendon tears are one of the most common causes of shoulder pain. The supraspinatus tendon, which forms part of the rotator cuff muscles, can . surgeon, like Dr. Sushil Pant in Sydney, will evaluate your shoulder through physical examination and diagnostic tests, such as MRI scans. This helps determine the extent of the tear, and . A rotator cuff tear causes shoulder pain and makes arm movements difficult. Your risk of a tear increases with age. . Diagnosis and Tests. How is a rotator cuff tear diagnosed? Your healthcare provider will perform a physical exam to check for shoulder tenderness, range of motion and arm strength. . Introduction. Shoulder pain is one of the most common musculoskeletal disorders. The incidence of shoulder disorders was predicted at 11.2/1000 patients/year, with most cases originating from rotator cuff tears [1-3], which are usually due to subacromial impingement syndrome (SIS).SIS is the most common pathology that causes shoulder pain, and the .The most common condition that mimics a rotator cuff tear is shoulder stiffness or a frozen shoulder. This condition is characterized by reduced range of motion — the shoulder will only move so far before starting to hurt. It is common for a patient to develop a stiff and painful shoulder with no injury.
Incidence is estimated to be around 6.7% for complete thickness supraspinatus tears 2,3. Clinical presentation. Patients will present with shoulder pain and tenderness along the supraspinatus tendon. Many might present with a limited range of motion, especially in abduction. The Jobe test can be performed to elicit any injury to this tendon 2 . The O’Brien test can help diagnose a tear in the top or superior part of your labrum. A superior labrum tear is also called a SLAP tear, which stands for superior labrum, anterior to posterior. The O’Brien test can also rule out other problems, such as: Rotator cuff tear. Shoulder impingement syndrome.Individuals with a tear of the supraspinatus may complain of tenderness over the greater tuberosity, pain located in the anterior shoulder and symptoms radiating down the arm. . The diagnostic value of the combination of patient characteristics, history, and clinical shoulder tests for the diagnosis of rotator cuff tear. Journal of . - Jobe test of supraspinatus strength - External rotation test - Gerbers test - Internal lag test for rotator cuff tear - External lag test for rotator cuff tear - Neer test for shoulder impingement - Hawkins Kennedy test for shoulder impingement - Scapular repositioning test - Scapular assistance test - Sulcus sign - Apprehension relocation tests
Supraspinatus assessment (empty can test/Jobe’s test) This clinical test assesses the function of the supraspinatus muscle. 1. Abduct the patient’s arm to 90° and then angle the arm forwards by approximately 30° so that the shoulder is in the plane of the scapula. 2. Internally rotate the arm so that the thumb points down towards the .
special tests for supraspinatus tear
Transex E Travestis Estado do São Paulo. Encontros casuais adultos Estado do São Paulo em Skokka.com Encontre sexo na sua cidade. Mais de 500,000 classificados grátis em .
shoulder supraspinatus tear test|full thickness tear supraspinatus